Artificial Intelligence (AI) is one of the current hot topics in Computer Science and society more broadly. It is at the heart of everyday technology like navigation and photography apps, powers internet-scale algorithms for recommending purchases and content to view, and will enable huge future impact through autonomous cars and robots.
 AI is the study of the nature of intelligence by building computer systems, and the application of these insights in solving real-world problems.
AI is the study of the nature of intelligence by building computer systems, and the application of these insights in solving real-world problems.
AI research at Birmingham covers a wide range of both theoretical and applied AI, including:
- Robotics – Birmingham has one of Europe’s leading robotics labs, where undergraduates and researchers work to make robots that navigate, speak, see, learn, build maps, and manipulate new objects. Their work is being applied in applications from autonomous driving to warehouse logistics to nuclear decommissioning.
- Machine Learning techniques are causing a revolution in computing, thanks to the large datasets and computing power now available via the web. At Birmingham we have machine learning experts working in robotics, computer vision, big data, and analysing brain signals, galaxy formation, web browsing behaviour and much more.
- Computer Vision – this includes all aspects of understanding images, including tracking people in video, object recognition, face detection, and understanding medical images (fMRI, X-rays, ultrasound).
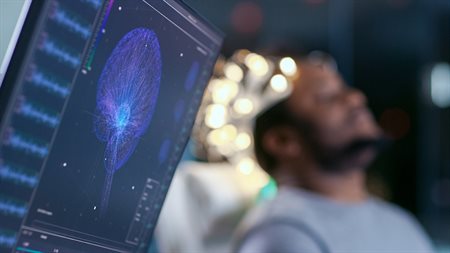
- Neural Networks are inspired by the stimulation of neurons in the brain, and are at the centre of deep learning, which is revolutionising what machines are capable of. At Birmingham we run a world-leading Centre for Computational Neuroscience where such models are compared to human behaviour and brain function.
- Natural Language Processing – this means producing computer systems that can communicate in human languages. At Birmingham we are finding new ways for computers to understand the emotion of social media posts, and process scientific documents to create new resources for learning. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is one of the current hot topics in Computer Science and society more broadly. It is at the heart of everyday technology like navigation and photography apps, powers internet-scale algorithms for recommending purchases and content to view, and will enable huge future impact through autonomous cars and robots.
- Nature-inspired Computing creates algorithms using ideas from natural systems, such as evolution, ant foraging, molecular computation, and cell signalling. Our researchers apply these ideas to problems from designing aircraft wings to discovering new drugs.
Applications of AI
There are a huge number of uses for AI technology, including:
- Fraud detection systems which use neural networks and machine learning to detect stolen credit cards by learning customer behaviour.
- Automated trading algorithms that outperform the market by evolving their stock trading strategies.
- Self-driving cars, including collision avoidance, self-parking, navigation by vision, and complete autonomous driving are now entering the car market.
- Genetic algorithms that are used in scheduling to find out the most efficient way to roster staff or allocate resources.
- Medical decision support systems which are now increasingly used by clinicians to support clinical decision-making.
- Forensic analysis of CCTV images using AI vision technology which is being developed to catch criminals.
AI teaching
Our degree programmes provide you with the opportunity to develop a strong theoretical grounding in AI plus many opportunities to put this theory in to practice. Our AI teaching includes:
- Artificial Intelligence – a general module covering the fundamental AI representations and algorithms used today. This covers search and machine learning. It further includes robot programming where you have opportunities to implement AL algorithms on real robot hardware. For example, our students work on robots collaboratively solving problems.
- Mathematical Modelling and Decision Making – AI and machine intelligence are increasingly reliant on models of the world that account for uncertainty - probabilistic models. For example, in medicine, we are constantly faced with problems of disease diagnosis (or trying to establish the cause of a disease), and we only have probabilistic information about the most likely disease (or the most likely cause). This module will look at the tools and principles behind progress in similarly challenging problems.
- Machine Learning and Intelligent Data Analysis – you will gain an understanding of the core concepts, methods, and algorithms for analysing and learning from data, illustrated through a set of methods widely used in practice.
- Complex Adaptive Systems - many natural and artificial systems, such as brains or the internet, are characterised by complex behaviours that emerge from interactions between a large number of simpler components. These systems are collectively called complex adaptive systems (CAS). In this module, we will study the basic concepts, theories and methods for designing and understanding CAS. Example topics covered include artificial life, evolutionary computation, swarm intelligence and artificial neural networks.
- Computer Vision and Imaging – we cover all the steps needed to transform an image into the structural and semantic entities necessary to understand its contents. We teach subjects such as object recognition, categorisation, segmentation, registration, stereo vision, motion analysis, and tracking.